PERSPECTIVE: Every Generation Has Something to Teach - Why You Should Leverage All Levels of Knowledge in the Workplace
/by Kim Sirois Pita Have you noticed the dynamics of your work environment changing right before your eyes? Our technology-connected youth are swooping in with their infinite wisdom and scooping up the jobs once occupied by our elders. We are in the midst of a true generational shift stemming from the reality of the graying of America.
This shift has brought five generations together into the workforce for the first time spanning from our aspiring teens to our active seniors. As these generations naturally converge, it becomes even more necessary to understand the vast differences among them, and how each can share essential knowledge.
Gloria Steinem, an 81-year-old pioneer of the feminist movement, said it best: “We need to remember across generations there is as much to learn as there is to teach.”
Take for example The Intern movie featuring Anne Hathaway and Robert DeNiro. The 2015 movie cleverly unveils work style differences between boomers and millennials by putting 20-something Hathaway in charge of 60-something DeNiro at her thriving Internet company.
While waiting for an assignment from the “boss lady,” he reads the morning paper from his brown leather attaché case. Hathaway barely notices him as she pedals her retro bicycle through the swanky open-space office, doing business from a blue tooth apparatus stuck to her ear.
 Hathaway’s character is a smart, savvy young businesswoman, who doesn’t want to face overwhelming feelings of stress and unease. But she is being forced to recognize her lack of business management experience by her company’s Board of Directors. When Hathaway finally realizes DeNiro’s value, she opens herself up to learning from him, and even yields to his advice on major business decisions.
Hathaway’s character is a smart, savvy young businesswoman, who doesn’t want to face overwhelming feelings of stress and unease. But she is being forced to recognize her lack of business management experience by her company’s Board of Directors. When Hathaway finally realizes DeNiro’s value, she opens herself up to learning from him, and even yields to his advice on major business decisions.
Learning, most definitely, is a two-way street. When you change your attitude and free your mind to take it all in and refrain from the “know it all” attitude, an amazing behavioral shift and transfer of knowledge begins to occur between people of all ages.
While teaching a generational marketing class at Capital Community College, I remember an adult student commenting about the younger generations who seemed to look down on the older generations in her office. She used the word “aloof” to describe how the young professionals felt about the baby boomers.
By the end of the class, this student realized that perhaps she and her coworkers never fully embraced the talents of the younger generation, and perhaps they were being a bit dismissive of what they could contribute. Thanking me for opening her eyes, she went back to the state office with a new outlook — one where learning across generations should be embraced rather than dismissed.
Younger generations are entering the workforce with far greater expectations than their older counterparts. They are highly educated, information hounds with 24-hours access to knowledge. An afternoon at the library has since been replaced with a 15-minute Google search from anywhere, at any time — and they have harnessed the power of this.
The term “paying your dues” is no longer relevant in our changing workforce. Instead it is more about the skills and talents you can bring to the job. Sure, this will cause resentment among many, but it is the new reality that, ultimately, needs to be accepted to maintain a happy and cohesive workplace environment.
And not only do employees need to play nice in the sandbox during the work day, company leaders needs to understand and address the communication and work style differences across generations. They need to encourage collaboration and knowledge swapping between generations.
Gen X (age 34 to 45) and Millennials (age 18 to 33) tend to communicate in sound bytes using email, social media and mobile, while the older generations (Silent and G.I.) prefer lengthy detailed explanations. Baby Boomers (age 46 to 64) fall somewhere in the middle — they want details, but they are often time-challenged to absorb too much, often balancing work, home, kids, volunteer commitments and elderly parents.
While companies are trying to adapt to varying preferences among the generations, immediate change is not always possible. Company leaders need to balance what will work best for the business and its evolving employee population.
_____________________________________
Kim Pita is founder of Pita Peaces and former managing principal of The Pita Group. She is a transformational brand leader who works with industry pioneers and family owned businesses in transition. She takes them from a place of chaos and uncertainty to harmony and prominence. Kim serves as chair of CBIA’s Small Business Advisory Council and vice chair of the Mental Health Connecticut Board of Directors.
PERSPECTIVE commentaries by contributing writers appear each Sunday on Connecticut by the Numbers.
LAST WEEK: Progress Made on Regional Cooperation


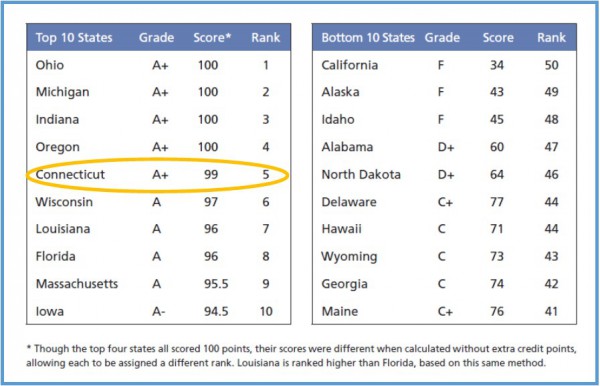
 Based on an inventory of the content and ease-of-use of states' transparency websites, the report assigns each state a grade of “A+” to “F.” The leading states with the most comprehensive transparency websites are Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Oregon, and Connecticut, with each receiving an A+ grade.
Based on an inventory of the content and ease-of-use of states' transparency websites, the report assigns each state a grade of “A+” to “F.” The leading states with the most comprehensive transparency websites are Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Oregon, and Connecticut, with each receiving an A+ grade.
 inue to improve, the states that most distinguished themselves as leaders in spending transparency are those that provide access to types of expenditures that otherwise receive little public scrutiny. Only 11 states- including Connecticut - provide checkbook-level information that includes the recipients of each of the state’s most important subsidy programs.
inue to improve, the states that most distinguished themselves as leaders in spending transparency are those that provide access to types of expenditures that otherwise receive little public scrutiny. Only 11 states- including Connecticut - provide checkbook-level information that includes the recipients of each of the state’s most important subsidy programs.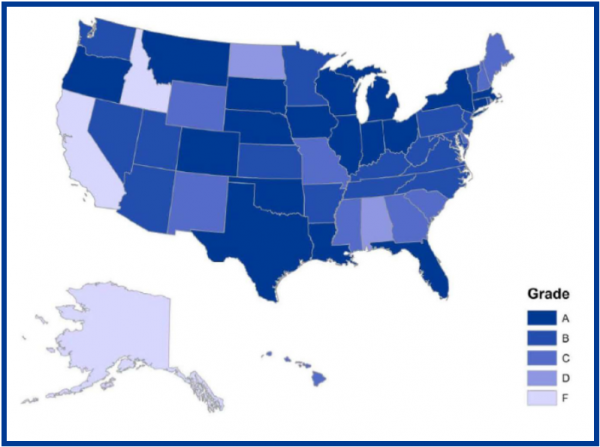






 for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center.
for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center. In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.
In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.


 In an article appearing in this week’s
In an article appearing in this week’s 




 The D5 final report features stories about leaders in foundations and other philanthropic organizations taking meaningful action to advance DEI. “Storytelling is one of the most powerful ways to inspire action and change. We hope people working within foundations—whether they are a CEO, an HR manager or a program officer—draw on the important lessons from these stories, and apply them to their own unique situations,” said Kelly Brown, D5 Director. Kelly also cited statistics indicating that “when companies commit themselves to diverse leadership, they are more successful. Foundations and nonprofits,” she said, “have the opportunity to take a page from successful business playbooks.”
The D5 final report features stories about leaders in foundations and other philanthropic organizations taking meaningful action to advance DEI. “Storytelling is one of the most powerful ways to inspire action and change. We hope people working within foundations—whether they are a CEO, an HR manager or a program officer—draw on the important lessons from these stories, and apply them to their own unique situations,” said Kelly Brown, D5 Director. Kelly also cited statistics indicating that “when companies commit themselves to diverse leadership, they are more successful. Foundations and nonprofits,” she said, “have the opportunity to take a page from successful business playbooks.”



























