Connecticut Road, Rail, Bridge Infrastructure Continues to Earn Scrutiny
/Often described as “an accident waiting to happen,” the condition of Connecticut’s road, rail and bridge infrastructure continues to earn scrutiny from policy makers and the public. In the transportation-congested Northeast corridor, the intertwining highway and rail bridges, often stacked above and below one another or alongside each other, underscore the potential consequences of infrastructure failure. The state legislature is poised this week to devote a portion of the state sales tax in the coming years to the start of a long-term transportation infrastructure revitalization plan proposed by Gov. Malloy.
“Improving safety features on Connecticut’s roads and highways would likely result in a decrease in the state’s traffic fatalities and serious crashes,” a report in December 2014 by TRIP, a nonprofit organization that researches transportation issues, pointed out. “It is estimated that roadway features are likely a contributing factor in approximately one-third of all fatal and serious traffic crashes.”
The report noted that “highways are vitally important to continued economic development in Connecticut, particularly to the state’s tourism, farming, agriculture, manufacturing, and insurance industries. As the economy expands, creating more jobs and increasing consumer confidence, the demand for consumer and business products grows. In turn, manufacturers ship greater quantities of goods to market to meet this demand, a process that adds to truck traffic on the state’s highways and major arterial roads.”
Amtrak's ridership through the Northeast corridor, including Connecticut, is up 50 percent since 1998, boosted by the introduction of high-speed trains. A record 11.6 million riders rode Amtrak in the corridor in fiscal year 2014, the Associated Press recently reported. Commuter railroads that rely heavily on the rail corridor, like the Metro-North Railroad serving New York and Connecticut, also have been breaking ridership records.
That same report, however, indicated that half of the route's 1,000 bridges are around a century old. Not all are at the end of their useful lives, but at current funding levels, it would take 300 years to replace all of them, according to the Northeast Corridor Commission of transportation officials, the AP reported.
“The terrible tragedy in Philadelphia is only the most recent reminder of the tremendous backlog of basic repairs and safety upgrades we have accumulated as the result of years of underinvestment in this critical asset,’’ U.S. Senator Chris Murphy said recently. He’s proposing that $555.8 million in the president’s budget for Northeast Corridor rail improvements to be directed at rail-safety projects only. Murphy calls the $555.8 million a “drop in the bucket,’’ noting that the Northeast Corridor repair backlog currently stands at $21.1 billion.
 As one example, state officials are working on a plan to replace a swinging bridge over the Norwalk River, built in 1896. "As a piece of engineering, it's just amazing," John Bernick, assistant rail administrator for the state Department of Transportation told the AP. "But, it's certainly reached its retirement age.” The computer that operates the bridge is from the 1980’s, and replacing the bridge could cost as much as $650 million.
As one example, state officials are working on a plan to replace a swinging bridge over the Norwalk River, built in 1896. "As a piece of engineering, it's just amazing," John Bernick, assistant rail administrator for the state Department of Transportation told the AP. "But, it's certainly reached its retirement age.” The computer that operates the bridge is from the 1980’s, and replacing the bridge could cost as much as $650 million.
Last October state officials announced a plan, using state and federal funds, for the design and replacement of that century-old Walk Bridge, which malfunctioned in two separate incidents within a two week period last summer. The project is be funded with 34 percent state funds and 66 percent federal funds. Officials anticipate the design for the replacement bridge, which began last July, to be complete by 2016. With a contract bid package complete by late 2016, construction of the replacement bridge could begin in 2017 with a completion date in 2020.
A report in 2010 from the Federal Highway Administration found that out of 4,186 bridges in Connecticut, 378 bridges were considered structurally deficient and 1,028 bridges were considered functionally obsolete. In 2008, a report by TRIP, indicated that the average age of bridges in Connecticut was 40 years, and that 46 percent of the state’s bridges were built prior to 1960. The organization’s updated report, in December 2014, found that 35 percent of Connecticut bridges are in need of repair, improvement or replacement. Ten percent of the state’s bridges are structurally deficient and 25 percent are functionally obsolete.
Annually, $143 billion in goods are shipped from sites in Connecticut and another $119 billion in goods are shipped to sites in Connecticut, mostly by truck, the 2014 TRIP report indicated. Forty-one percent of Connecticut’s major locally and state-maintained roads and highways have pavements in poor condition, while an additional 41 percent of the state’s major roads are rated in mediocre or fair condition and the remaining 18 percent are rated in in good condition.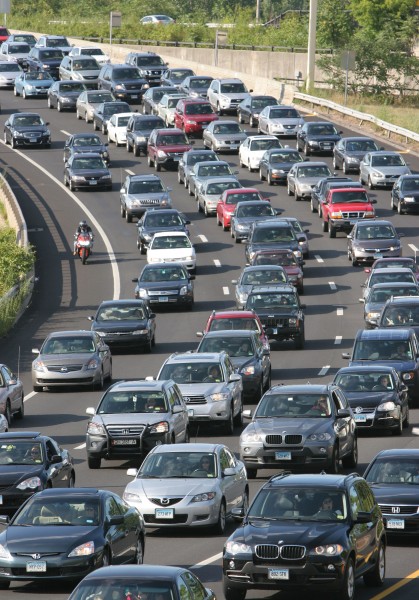
In addition, Connecticut has more than 3,400 bridges and culverts on municipally maintained roads, according to the state Department of Transportation. Construction and maintenance of these expensive structures is the responsibility of the cities and towns who own them. The state legislature, which is scheduled to adjourn on Wednesday, is considering a proposal that would increase the available funds under the State Local Bridge Program to assist local municipalities for FY 2016 applications to $15 million and would add $10 million for FY 2017 applications.
The TRIP report concluded that “making needed improvements to Connecticut’s roads, highways and bridges could provide a significant boost to the state’s economy by creating jobs in the short term and stimulating long-term economic growth as a result of enhanced mobility and access,” warning that “without a substantial boost in federal, state and local highway funding, numerous projects…will not be able to proceed, hampering the state’s ability to improve the condition of its transportation system and to enhance economic development opportunities in the state.”


 At the risk of sounding ponderous, the First Amendment creates a lot of situations like this, although they often pose tensions that are much more treacherous.
At the risk of sounding ponderous, the First Amendment creates a lot of situations like this, although they often pose tensions that are much more treacherous. ent project on Twitter, where she is posting, one line at a time, the text of the novel “Gone With the Wind.” They object to the novel’s tolerance of racism.
ent project on Twitter, where she is posting, one line at a time, the text of the novel “Gone With the Wind.” They object to the novel’s tolerance of racism. The July event is part of a year-long effort to listen, learn, and share with older adults, their families, their caregivers, community leaders, and experts in the aging field on how to best address the changing landscape of aging in the coming decade, officials said. Since the 1960’s the
The July event is part of a year-long effort to listen, learn, and share with older adults, their families, their caregivers, community leaders, and experts in the aging field on how to best address the changing landscape of aging in the coming decade, officials said. Since the 1960’s the 
 ment; how to remain healthy as we age; what types of services and supports can help older Americans remain independent in the community as we age; and how to support this care and the caregivers who provided it; and how to protect older Americans from financial exploitation, abuse and neglect.
ment; how to remain healthy as we age; what types of services and supports can help older Americans remain independent in the community as we age; and how to support this care and the caregivers who provided it; and how to protect older Americans from financial exploitation, abuse and neglect.
 Iowa Governor Terry Branstad provided opening remarks at Wednesday’s session, followed by Malloy’s keynote address. Branstad, a Republican, and Malloy, a Democrat, were re-elected by voters in their respective states last fall.
Iowa Governor Terry Branstad provided opening remarks at Wednesday’s session, followed by Malloy’s keynote address. Branstad, a Republican, and Malloy, a Democrat, were re-elected by voters in their respective states last fall.


 For the first time in the history of the awards program, a state agency was also selected to receive an award. The CT Department of Transportation received a special award for Starting a Revolution: Integration of Land Use and Transit in recognition of the progressive nature of CTfastrak, the bus rapid transit system opened earlier this year. The awards jury that selected the winners gave the award because they felt the new busway represents a cultural shift in how Connecticut views transit, and wanted to acknowledge the future promise of transit oriented development that will hopefully result around the station locations.
For the first time in the history of the awards program, a state agency was also selected to receive an award. The CT Department of Transportation received a special award for Starting a Revolution: Integration of Land Use and Transit in recognition of the progressive nature of CTfastrak, the bus rapid transit system opened earlier this year. The awards jury that selected the winners gave the award because they felt the new busway represents a cultural shift in how Connecticut views transit, and wanted to acknowledge the future promise of transit oriented development that will hopefully result around the station locations.


 mework, or take an elderly parent to a doctor’s appointment.” In half of all families with children, women are the primary or co-breadwinner, the report indicates, and low-income families are particularly likely to have all parents in the labor force.
mework, or take an elderly parent to a doctor’s appointment.” In half of all families with children, women are the primary or co-breadwinner, the report indicates, and low-income families are particularly likely to have all parents in the labor force.
 The analysis pointed out that nationally “many workers lack access to even the most basic supports such as earned sick days and job-protected paid parental leave. Quality child care is also out of reach for many families because it is not affordable. Women are the large majority of family caregivers, and in the absence of reliable family supports, too many women are forced to make difficult decisions between keeping their jobs and caring for their family members.”
The analysis pointed out that nationally “many workers lack access to even the most basic supports such as earned sick days and job-protected paid parental leave. Quality child care is also out of reach for many families because it is not affordable. Women are the large majority of family caregivers, and in the absence of reliable family supports, too many women are forced to make difficult decisions between keeping their jobs and caring for their family members.” (U.S. Department of Labor Women’s Bureau 2015). The report indicates that Connecticut has 392,974 “breadwinner mothers in households with children under 18,” using 2013 data, ranking the state 25th in the nation at 29 percent.
(U.S. Department of Labor Women’s Bureau 2015). The report indicates that Connecticut has 392,974 “breadwinner mothers in households with children under 18,” using 2013 data, ranking the state 25th in the nation at 29 percent.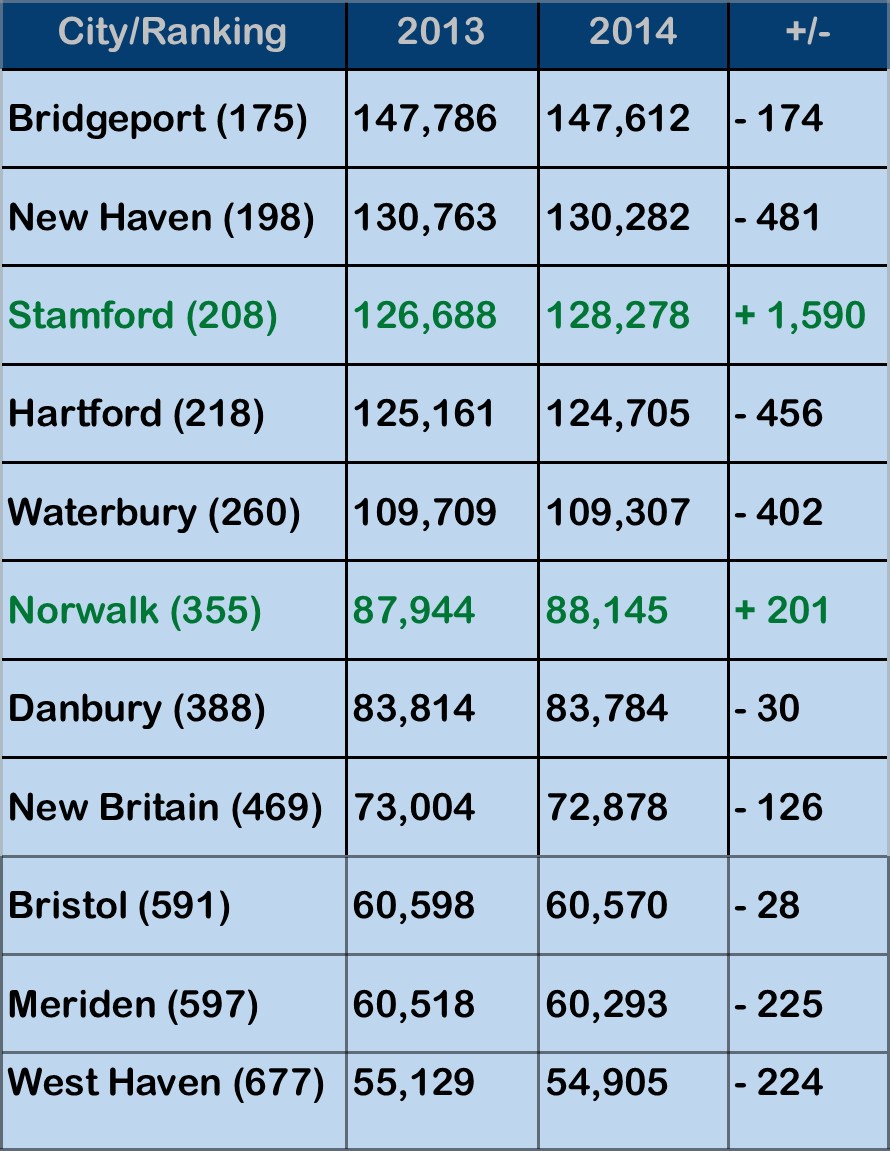 Over the past four years, population also grew in Hartford, New Haven, Stamford, Danbury and Norwalk, but declined in some of the state’s other large municipalities, including Waterbury, New Britain, Meriden and West Haven.
Over the past four years, population also grew in Hartford, New Haven, Stamford, Danbury and Norwalk, but declined in some of the state’s other large municipalities, including Waterbury, New Britain, Meriden and West Haven. wed the gap between the two cities to 2,004. Just four years ago, the population differential was 7,075. Stamford passed Hartford to rank as the state’s third largest city three years ago.
wed the gap between the two cities to 2,004. Just four years ago, the population differential was 7,075. Stamford passed Hartford to rank as the state’s third largest city three years ago.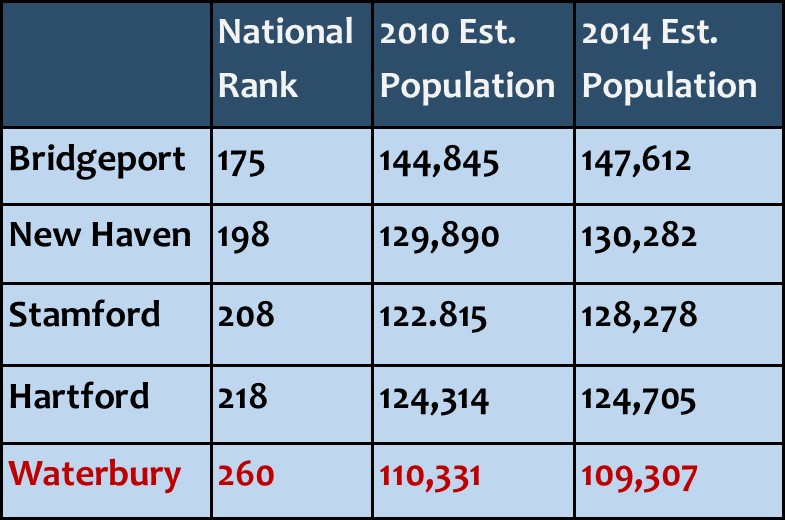 according to the census data, while Bristol (number 591) saw a slight uptick of just under 100 residents, from 60,477 to a 60,570. Meriden (number 597) saw population slip from 60,868 to 60,293. West Haven, the 677th most populous city in the nation, also experienced a drop in populations, from 55,565 to 54,905.
according to the census data, while Bristol (number 591) saw a slight uptick of just under 100 residents, from 60,477 to a 60,570. Meriden (number 597) saw population slip from 60,868 to 60,293. West Haven, the 677th most populous city in the nation, also experienced a drop in populations, from 55,565 to 54,905.

 The organization also accepts
The organization also accepts 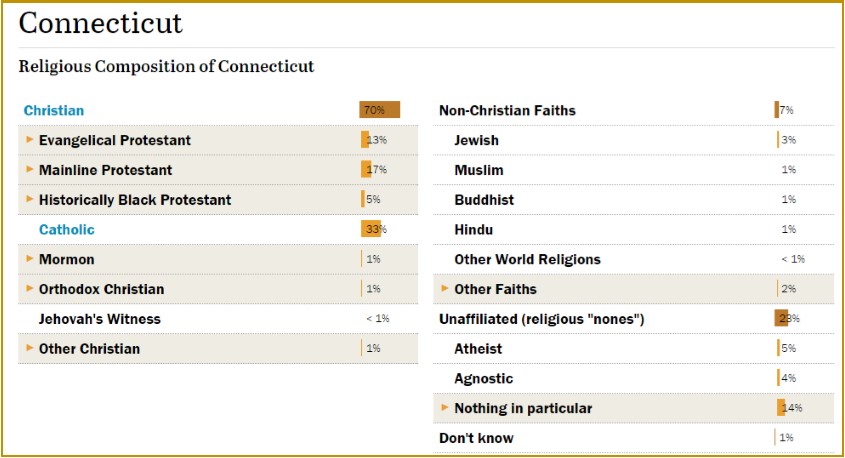 While the drop in Christian affiliation is particularly pronounced among young adults nationwide, it is occurring among Americans of all ages. The same trends are seen among whites, blacks and Latinos; among both college graduates and adults with only a high school education; and among women as well as men, according to the Pew data.
While the drop in Christian affiliation is particularly pronounced among young adults nationwide, it is occurring among Americans of all ages. The same trends are seen among whites, blacks and Latinos; among both college graduates and adults with only a high school education; and among women as well as men, according to the Pew data.


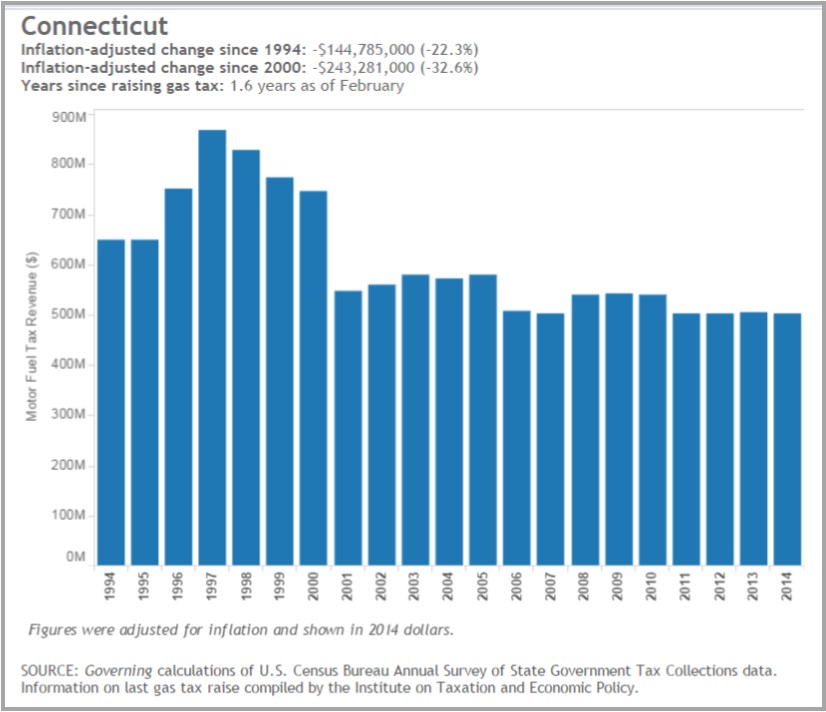 In Connecticut, the inflation-adjusted change is a reduction of in the value of the dollars provided by the tax of 32.6 percent since 2000 and 22.3 percent since 1994, according to the Governing analysis, using data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Earlier this year, Governor Malloy announced a two-part transportation plan consisting of a
In Connecticut, the inflation-adjusted change is a reduction of in the value of the dollars provided by the tax of 32.6 percent since 2000 and 22.3 percent since 1994, according to the Governing analysis, using data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Earlier this year, Governor Malloy announced a two-part transportation plan consisting of a 


























